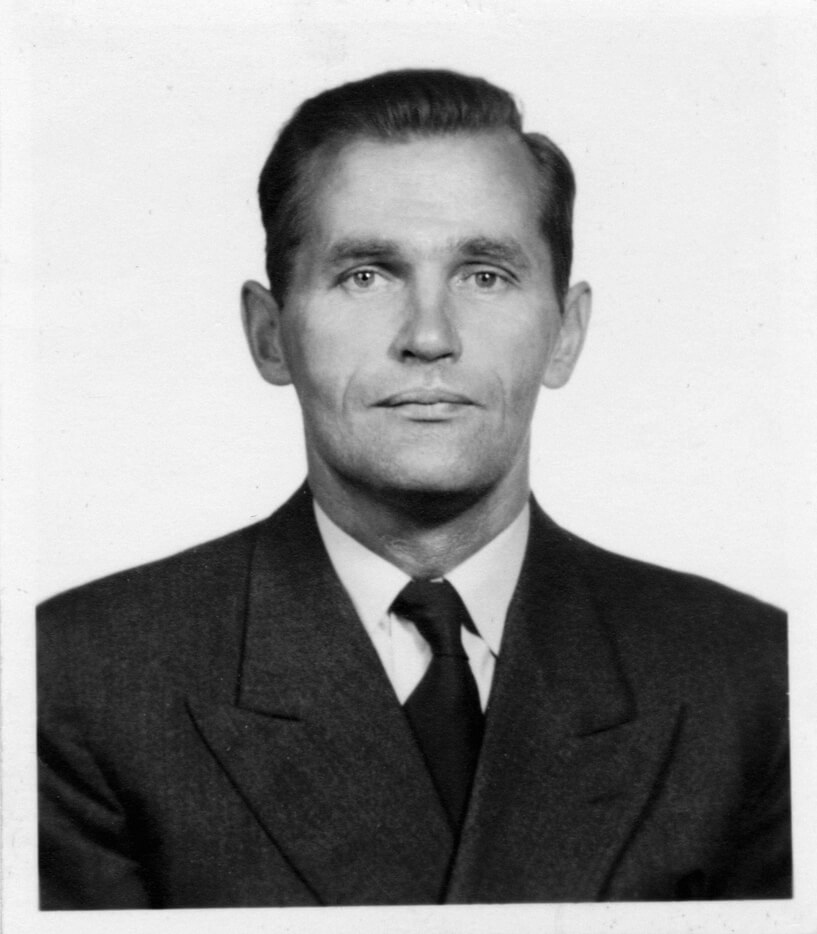
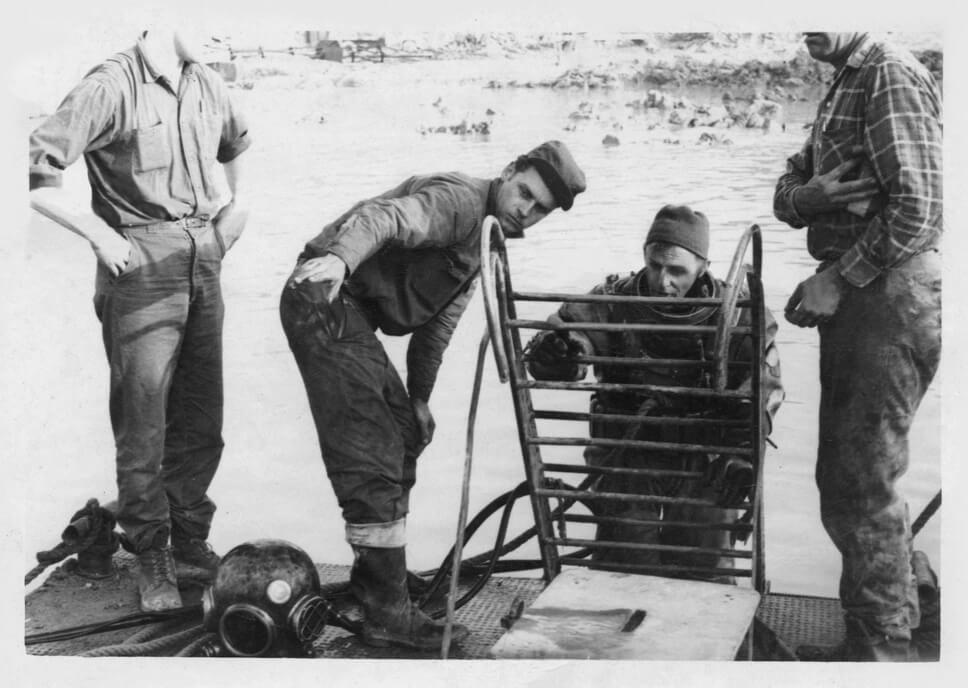
Fricis Rudzītis
(1897 – 1957)



Fricis Rudzītis was born in Tadaiki, Priekule Municipality. In 1915, his family relocated to St. Petersburg. After finishing Nikolai Gymnasium, F. Rudzītis continued his studies at the then prestigious St. Petersburg Electrotechnical Institute, graduating with a diploma in electrical engineering in 1922. In 1923, Rudzītis returned to Latvia. The diploma obtained in Soviet Russia was not recognised in Latvia, so he enrolled at the Faculty of Mechanics at the University of Latvia. In 1926, he was the first one at the University of Latvia to receive an electrical engineer’s diploma. In the following years, Fricis Rudzītis improved his knowledge abroad. In 1927, he worked at a transformer building in the Siemens Nuremberg factory in Germany, and from 1928 to 1930 he was employed as an engineer at Metropolitan-Vickers in England, which manufactured generators, steam turbines, electric switchgear and transformers in the first half of the 20th century. From 1930, F. Rudzītis worked as an engineer at the VEF factory (Riga). In 1936, when the construction of Kegums Power Plant was launched, Rudzītis was one of the first to start work at the construction inspectorate. He was responsible for inspecting the equipment supplied for the construction of the power plant. From 1940, he was Head of the Technical Division of the Production Directorate at the State Electricity Enterprise Kegums. Under the supervision of F. Rudzītis, 88 kV power line and transformer substation projects of the Latvian power grid were developed and construction of power lines was carried out. In 1946, Fricis Rudzītis was a senior engineer of the Production Engineering Division at the Energy Enterprises Administration Latenergo under the Latvian SSR Local Industry People’s Commissariat (from 11 April 1946 – the Latvian State Energy Administration Latvenergo under the Ministry of Power Plants of the USSR) and later he was employed as the chief engineer of the Design and Development Office. Until 1957, Fricis Rudzītis directed the construction of 110/20/6 kV transformer substations and the building of 88 kV and 110 kV power lines.
Otto Leimanis
(1884 – 1960)

Herberts Knolbahs – Tombergs
(1912 – 1981)




Gustavs Feigmanis
(1885 – 1942)


Mārtiņš Robs
(1874 – 1947)
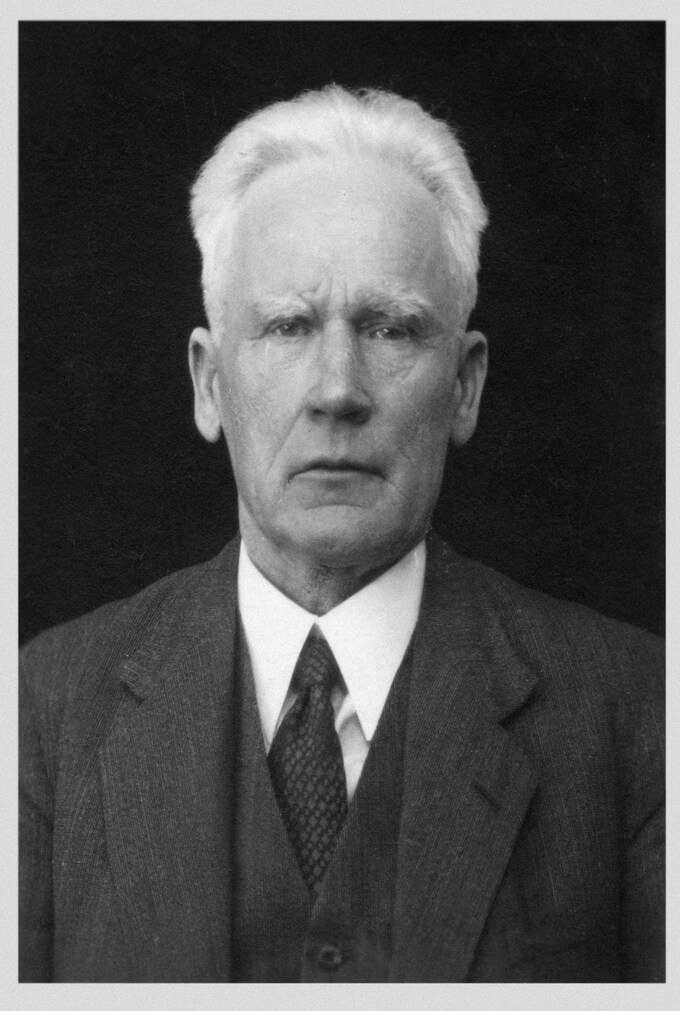
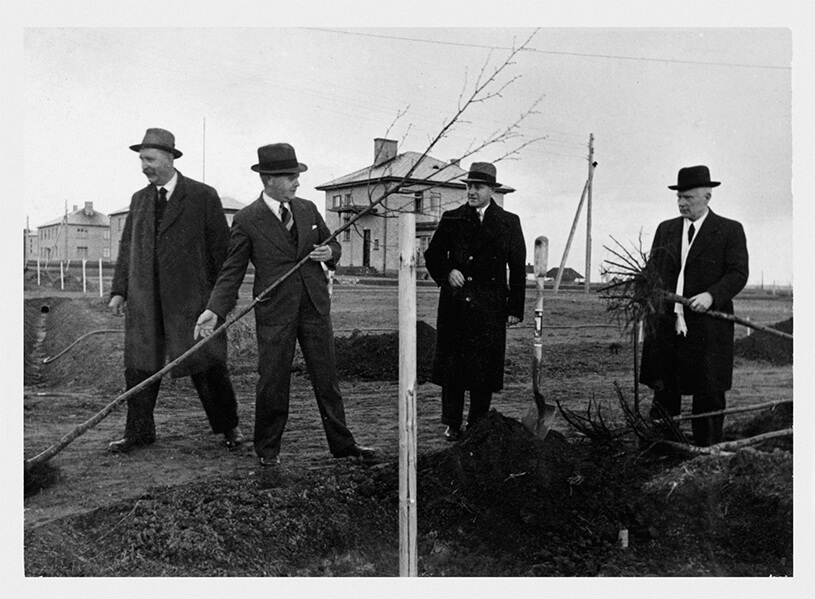
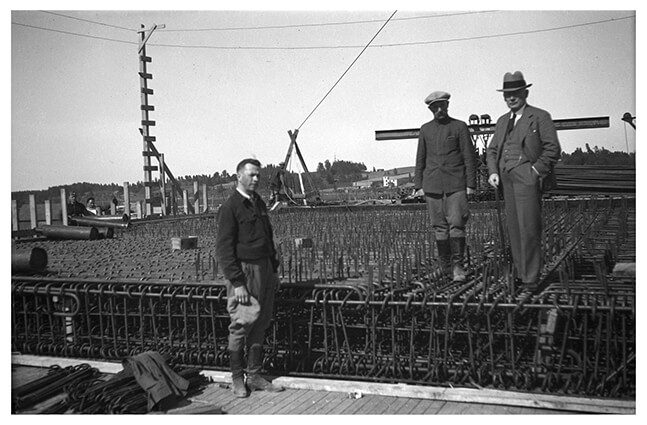




Pēteris Leonhards Stakle
(1881 – 1944)
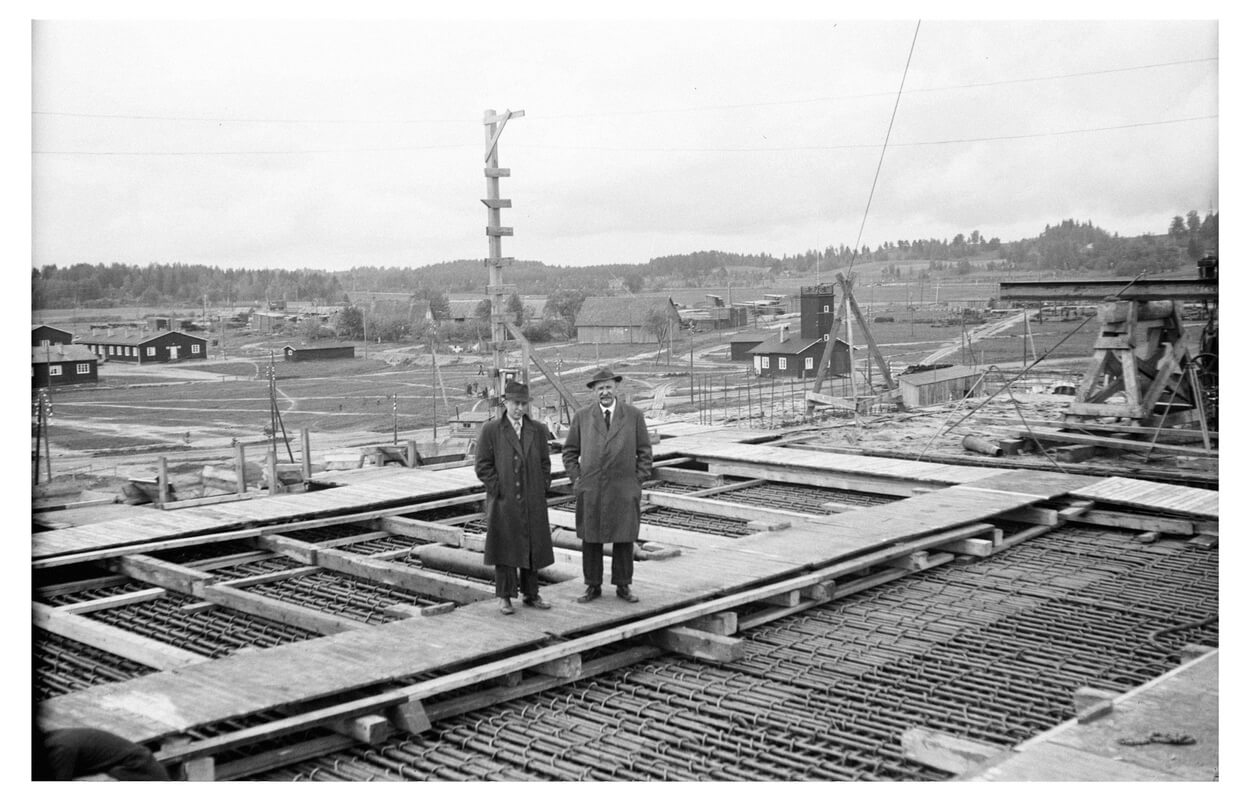
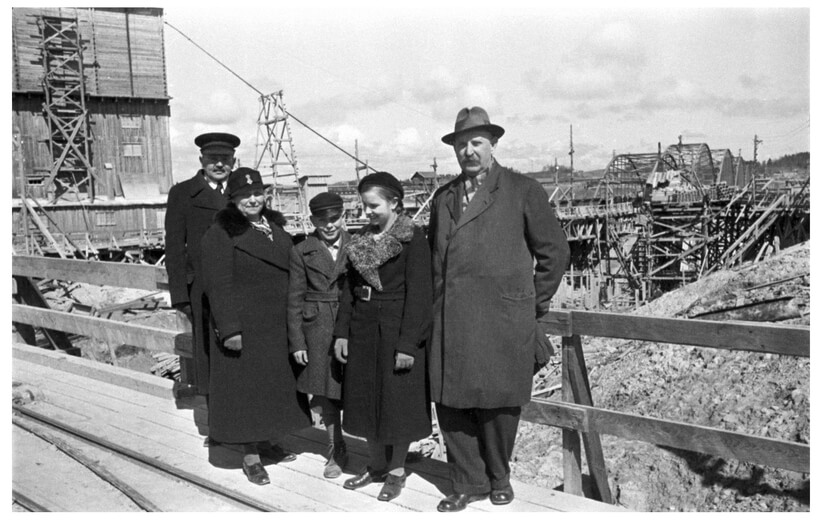


Pāvils Krasovskis
(1906 – 1945)



Edgars Kelders
(1900 – 1956)


Ēvalds Šics
(1902 – 1953)




Valentīns Pāvuls
(1905 – 1993)


